Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakahara, Masaumi; Watanabe, So; Ogi, Hiromichi*; Arai, Yoichi; Aihara, Haruka; Motoyama, Risa; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori; Kajinami, Akihiko*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.66 - 70, 2019/09
A wide variety of hazardous and radioactive liquid waste has generated derived from an advanced aqueous separation experiments in the Chemical Processing Facility. Therefore, they should be stabilized for the safety handling and management. In this study, we report a precipitation or an oxidation for hazardous materials, a solvent extraction for recovery of nuclear materials, and a concentration of solution by a freeze-drying method.
 C addition on thermophysical properties of austenitic stainless steel in a solid state
C addition on thermophysical properties of austenitic stainless steel in a solid stateTakai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.847 - 852, 2019/09
Narukawa, Takafumi; Amaya, Masaki
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.912 - 921, 2019/09
Amaya, Masaki; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Mihara, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.1048 - 1056, 2019/09
Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Makino, Takayoshi; Iso, Hidetoshi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Sato, Hisato; Fukasawa, Tomonori*; Fukui, Kunihiro*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.738 - 745, 2019/09
In the MOX fuel fabrication process, the dry grinding technology of mixed oxide pellets have been developed for the effective use of nuclear fuel materials. To develop a technology to control the particle size of dry recovered powder, the performance of the buhrstone mill and the collision plate type jet mill were studied using a simulated powder of particle size distribution about 500  m. We found that the particle size can be controlled at the range of about 250
m. We found that the particle size can be controlled at the range of about 250  m or less by both by adjusting the clearance between the grinding wheels of the buhrstone mill, and the clearance and elevation angle of the clarification zone of the collision plate type jet mill. And furthermore, the collision plate type jet mill is considered to be suitable for particle size control because the operating parameters of the classifier can be finely adjusted.
m or less by both by adjusting the clearance between the grinding wheels of the buhrstone mill, and the clearance and elevation angle of the clarification zone of the collision plate type jet mill. And furthermore, the collision plate type jet mill is considered to be suitable for particle size control because the operating parameters of the classifier can be finely adjusted.
Yamada, Yoshikazu; Shibanuma, Kimikazu
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.648 - 654, 2019/09
During a periodic inspection, multiple spot-like nuclear material contamination (maximum 21.7 Bq) was detected at the outer surface of a glove-box (GB) body used to install equipment for fabricating mixed oxide (MOX) fuel at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The inspection confirmed a total of 13 cracks passing through the thickness direction of the GB and a bleeding phenomenon was observed on the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cables in the GB. These cracks were judged as stress corrosion cracking induced by the generation of chlorine gas by irradiation of PVC cables lying against the inner surface of the GB.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.418 - 427, 2019/09
Eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
Mihara, Takeshi; Udagawa, Yutaka; Amaya, Masaki; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Kakiuchi, Kazuo
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.544 - 550, 2019/09
Sasaki, Yuji; Morita, Keisuke; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nakase, Masahiko*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.108 - 112, 2019/09
We attempted to separate An from Ln, and Am and Cm by the system including extractant and masking agent. The separation factor of Nd and Am was approximately 10 by TODGA-DTPA-BA and that of Am and Cm was over 3 by TODGA-DOODA(C2). Using these batch data, profiles of metal concentration with multi-step extractions proposed in this manuscript were demonstrated.
Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Udagawa, Yutaka; Mihara, Takeshi; Amaya, Masaki; Kakiuchi, Kazuo
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.551 - 558, 2019/09
Ota, Hirokazu*; Ohgama, Kazuya; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.30 - 39, 2019/09
 C addition on viscosity of austenitic stainless steel in liquid state
C addition on viscosity of austenitic stainless steel in liquid stateOta, Hiromichi*; Kokubo, Hiroki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.858 - 860, 2019/09
A viscosity measurement apparatus has been developed. It is known that the measurement of the viscosity of molten alloy at elevated temperatures is difficult due to the difficulty of handling for low viscosity fluids such as the stainless steel (SS)+B C alloy. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SS) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. This method is suitable for high temperature molten alloys. A crucible containing molten metal is suspended, and a rotational oscillation is given to the crucible electromagnetically. The oscillation was damped by the friction of molten metal. The viscosity is determined from the period of oscillation and the logarithmic decrement. The crucible was connected to a mirror block and an inertia disk made of aluminum, and whole of them was suspended by a wire made of platinum-13% rhodium alloy. A laser light is irradiated to the mirror. The reflection light is detected by the photo-detectors, and then, the logarithmic decrement of molten metal is determined. The viscosities of molten nickel and SS melts were measured up to 1823 K. In these results, the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SS were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and SS. By the equipment, the viscosity of molten SS+B
C alloy. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SS) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. This method is suitable for high temperature molten alloys. A crucible containing molten metal is suspended, and a rotational oscillation is given to the crucible electromagnetically. The oscillation was damped by the friction of molten metal. The viscosity is determined from the period of oscillation and the logarithmic decrement. The crucible was connected to a mirror block and an inertia disk made of aluminum, and whole of them was suspended by a wire made of platinum-13% rhodium alloy. A laser light is irradiated to the mirror. The reflection light is detected by the photo-detectors, and then, the logarithmic decrement of molten metal is determined. The viscosities of molten nickel and SS melts were measured up to 1823 K. In these results, the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SS were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and SS. By the equipment, the viscosity of molten SS+B C alloys are measured. The B
C alloys are measured. The B C concentration dependence of the viscosity of molten SS+B
C concentration dependence of the viscosity of molten SS+B C alloys is to be clarified.
C alloys is to be clarified.
 C addition on thermophysical properties of austenitic stainless steel in a liquid state
C addition on thermophysical properties of austenitic stainless steel in a liquid stateFukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.853 - 857, 2019/09
Thermophysical properties of molten mixture of 316L stainless steel (SS316L) and control-rod material (B C) are necessary for the development of computer simulation codes that describe core degradation mechanisms during severe accidents in nuclear power plants involving sodium-cooled fast reactors. The effect of B
C) are necessary for the development of computer simulation codes that describe core degradation mechanisms during severe accidents in nuclear power plants involving sodium-cooled fast reactors. The effect of B C addition to SS316L on the solidus and liquidus temperatures were first measured by differential scanning calorimetry. An electromagnetic levitation technique performed in a static magnetic field was used to measure the density, surface tension, normal spectral emissivity, specific heat capacity, and thermal conductivity of molten SS316L and SS316L containing B
C addition to SS316L on the solidus and liquidus temperatures were first measured by differential scanning calorimetry. An electromagnetic levitation technique performed in a static magnetic field was used to measure the density, surface tension, normal spectral emissivity, specific heat capacity, and thermal conductivity of molten SS316L and SS316L containing B C. The effects of B
C. The effects of B C addition to SS316L on the thermophysical properties were studied up to 10 mass%.
C addition to SS316L on the thermophysical properties were studied up to 10 mass%.
 C
CLiu, X.*; Morita, Koji*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.47 - 51, 2019/09
Investigation of the eutectic reaction in a core disruptive accident of sodium cooled reactor is of importance since reactor criticality will be affected by the change in reactivity after eutectic reaction. In this study, we performed 1st step of validation analysis using a fast reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III, with the developed model based on a new series of experiments, where a B C pellet was immersed into a molten stainless steel (SS) pool. The simulation results showed the general behavior of eutectic material formation measured in the experiments reasonably. The eutectic reaction consumes solid B
C pellet was immersed into a molten stainless steel (SS) pool. The simulation results showed the general behavior of eutectic material formation measured in the experiments reasonably. The eutectic reaction consumes solid B C and liquid SS, and then the liquid eutectic composition is produced at the early stage of reaction due to the high temperature of molten SS. Movement of the eutectic material in the molten pool leads to the redistribution of boron element. Molten SS pool then freezes to solid SS and movement of eutectic material is stopped by surrounding solid SS. Boron concentration in the pool was measured after molten SS freezes into a solid. Simulation results indicate that boron tends to accumulate in the upper part of the molten pool. This is attributed to the buoyancy force acting on lighter boron in the molten SS pool. A parametric study was also conducted by changing the initial temperature of B
C and liquid SS, and then the liquid eutectic composition is produced at the early stage of reaction due to the high temperature of molten SS. Movement of the eutectic material in the molten pool leads to the redistribution of boron element. Molten SS pool then freezes to solid SS and movement of eutectic material is stopped by surrounding solid SS. Boron concentration in the pool was measured after molten SS freezes into a solid. Simulation results indicate that boron tends to accumulate in the upper part of the molten pool. This is attributed to the buoyancy force acting on lighter boron in the molten SS pool. A parametric study was also conducted by changing the initial temperature of B C pellet and SS to investigate the temperature sensitivity on the eutectic reaction behavior.
C pellet and SS to investigate the temperature sensitivity on the eutectic reaction behavior.
Pham, V. H.; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki; Furumoto, Kenichiro*; Sato, Hisaki*; Ishibashi, Ryo*; Yamashita, Shinichiro
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.670 - 674, 2019/09
Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Yamane, Yuichi; Abe, Hitoshi
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.408 - 414, 2019/09
In a criticality accident, it is known that some kinds of radiolysis gases are generated mainly due to kinetic energy of fission fragments. Hydrogen gas (H ) is one of them, which is able to initiate explosion. The rate of H
) is one of them, which is able to initiate explosion. The rate of H generation and its total amount can be estimated from the number of fission per second if its G value is known. In this study, it was tried to estimate G value of hydrogen gas (G(H
generation and its total amount can be estimated from the number of fission per second if its G value is known. In this study, it was tried to estimate G value of hydrogen gas (G(H )) by using the H
)) by using the H concentration measured as time-series data in Transient Experiment Critical Facility (TRACY) which was carried out by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. There was time lag in the measured H
concentration measured as time-series data in Transient Experiment Critical Facility (TRACY) which was carried out by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. There was time lag in the measured H concentration from its generation. To overcome those problems, measured profile of H
concentration from its generation. To overcome those problems, measured profile of H concentration was reproduced based on a hypothetical model and its total amount was evaluated. Based on the model, the obtained G(H
concentration was reproduced based on a hypothetical model and its total amount was evaluated. Based on the model, the obtained G(H ) was 1.2.
) was 1.2.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kurata, Masaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Nozawa, Takashi*; Sato, Daiki*; Murakami, Nozomu*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.206 - 216, 2019/09
After the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant, research and development (R&D) program for establishing technical basis of accident-tolerant fuel (ATF) started from 2015 in Japan. Since then, both experimental and analytical studies necessary for designing a new light water reactor (LWR) core with ATF candidate materials are being conducted within the Japanese ATF R&D Consortium for implementing ATF to the existing LWRs, accompanying with various technological developments required. Until now, we have accumulated experimental data of the candidate materials by out-of-pile tests, developed fuel evaluation codes to apply to the ATF candidate materials, and evaluated fuel behavior simulating operational and accidental conditions by the developed codes. In this paper, the R&D progresses of the ATF candidate materials considered in Japan are reviewed based on the information available such as proceedings of international conference and academic papers, providing an overview of ATF program in Japan.
Morita, Keisuke; Suzuki, Hideya; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Takahashi, Yuya*; Omori, Takashi*; Kaneko, Masaaki*; Asano, Kazuhito*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.464 - 468, 2019/09
High level liquid waste (HLLW) contains several radionuclides with half-lives longer than 10 year. For reduce environmental burden of waste disposal, minor actinoids and long-lived fission products will to be partitioned and transmuted. JAEA and Toshiba developed process for recovering Se, Zr, Pd and Cs from HLLW. Solvent extraction for Zr with novel extractant,
year. For reduce environmental burden of waste disposal, minor actinoids and long-lived fission products will to be partitioned and transmuted. JAEA and Toshiba developed process for recovering Se, Zr, Pd and Cs from HLLW. Solvent extraction for Zr with novel extractant, 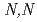 -didodecyl-2-hydroxyacetoamide (HAA) was detailed. The HAA system showed high selectivity for Zr, as indicated by the extraction order of Zr
-didodecyl-2-hydroxyacetoamide (HAA) was detailed. The HAA system showed high selectivity for Zr, as indicated by the extraction order of Zr  Mo
Mo  Pd
Pd  Ag
Ag  Sb
Sb  Sn
Sn  Lns
Lns  Fe. The extracted species was determined as Zr(HAA)
Fe. The extracted species was determined as Zr(HAA) (NO
(NO )
) (HNO
(HNO )
) . A continuous countercurrent extraction with HAA was applied to a simulated, concentrated HLLW after Pd, Se, and Cs removal, where the quantitative extraction of Zr and Mo was effectively demonstrated.
. A continuous countercurrent extraction with HAA was applied to a simulated, concentrated HLLW after Pd, Se, and Cs removal, where the quantitative extraction of Zr and Mo was effectively demonstrated.
Pastore, G.*; Gamble, K. A.*; Cherubini, M.*; Giovedi, C.*; Marino, A.*; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Van Uffelen, P.*; Veshchunov, M.*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.1038 - 1047, 2019/09
Oxidation-resistant iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) steels have been proposed for application as cladding materials in light water reactor fuel rods with improved accident tolerance. Within the Coordinated Research Project ACTOF of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), a fuel performance modeling benchmark for FeCrAl cladding behavior was conducted. During this effort, calculations were performed with various fuel performance codes for a set of fuel rod problems with FeCrAl steel as cladding material, and results were compared to each other.